Spray polyurethane foam (SPF) is a plastic product applied through spraying, commonly used to insulate buildings and seal cracks and gaps, improving energy efficiency and comfort. SPF insulation is known to resist heat flow and offers a highly effective solution in reducing unwanted air infiltration through cracks, seams, and joints.
Types of SPF
There are three primary types of SPF that can be used for insulation and other purposes:

Low-Density
Provides heat insulation and seals airflow through cracks, joints and seams by filling the cavities.
Learn More

Medium-Density
Often used for continuous insulation, interior wall cavity fill, and unvented attic applications.
Learn More

High-Density
A good choice for roofing or other exterior insulation because of its seamless, monolithic nature.
Learn More
Open-Cell vs. Close-Cell Spray Foam
Open-cell spray foam is spray foam that has cells which are deliberately left open, allowing for softer, more flexible foam. Open-cell spray foam is typically used in attics to seal cracks that can cause unwanted airflow. Additionally, open-cell spray foam provides acoustic controls by dampening soundwaves.
Closed-cell spray foam is spray foam that, as the name would suggest, has cells that are completely closed or encapsulated, making the foam denser and more rigid. Closed-cell spray foam provides greater thermal resistance than open-cell and is used in areas like attics and roofs to create a more consistent internal temperature and reduce energy consumption. Closed-cell spray foam also provides a moisture barrier where applied and creates a more resilient building.
Benefits of Spray Foam
Whether it is new construction, a renovation or a retrofit job, spray foam can be a great investment in your home. Spray foam can help prevent heat from flowing in and out of your home. It has air barrier properties that give it the unique ability to fill the gaps and holes that could be difficult to seal. No other insulation product on the market can match the performance of spray foam without utilizing additional products or materials.
Spray foam can help to lower energy bills through reducing heat loss or gain, eliminating air leaks, and improving energy efficiency. A recent analysis showed that homes with spray foam can reduce energy usage up to 5,638 kWh per year compared to the same home insulated and air sealed with other insulation. This amounts to a greenhouse gas reduction of 1,556 kg of CO2 per year, or a 33% reduction in the annual emissions of a car. Learn more about spray foam and reducing greenhouse gas emissions here.
Spray foam insulation and air barriers can reduce the carbon footprint from your home’s energy usage, which can help fight climate change. Even better, spray foam houses are energy efficient and resilient. Spray Foam can:
- Improve the comfort of your home
- Increase the energy efficiency of the home
- Reduce your energy bills
- Make your home stronger and more resilient
Spray foam may qualify you for tax credits or rebates.
Low-Density
Also known as open-cell-foam, low-density spray foam is spray applied to provide continuous insulation and an air-sealing barrier. Low-density SPF is also called ½ pound foam, as it weighs almost 0.5 lbs. per cubic foot. The foam’s open-cell structure gives some flexibility to the hardened foam.
Low-density foam is applied as low or high-pressure, two-component polyurethane spray foam. Low-density spray foam can be applied on walls, in unvented attics, to ducts and ceilings, and in vented attics and crawl spaces. It is known as an air barrier, but permeable to vapor and moisture. It is often used to fill cavities in walls during construction.
Due to its relatively large cell structure, low-density foam stays somewhat soft and flexible after curing. Low-density spray foam provides heat insulation and seals airflow through cracks, joints and seams by filling the cavities. In addition, this foam can help absorb sound thanks to its softer texture and open-cell structure.
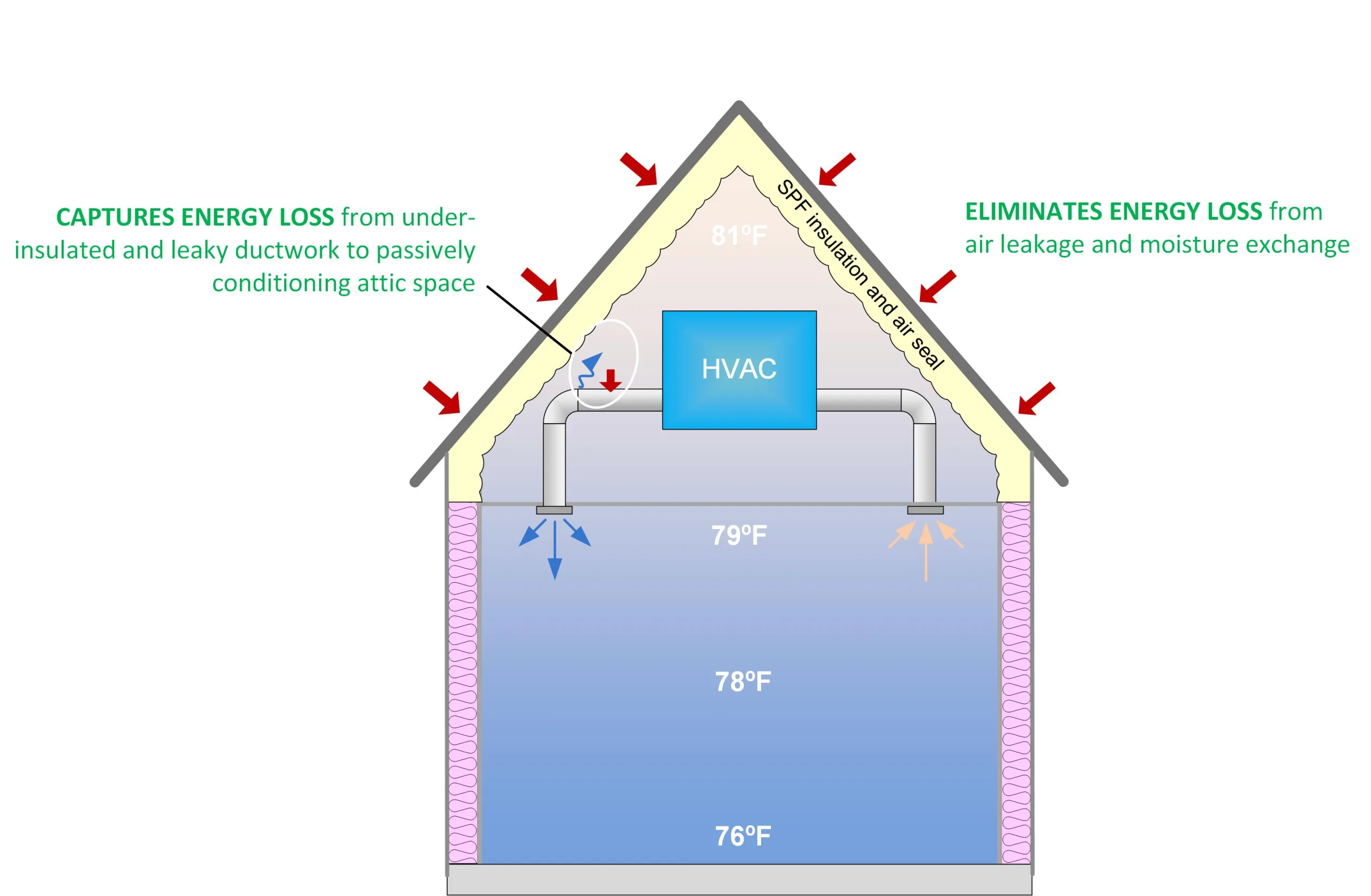
Medium-Density
Medium-density foam is applied as low- or high-pressure two-component spray foam. Medium-density foam offers specific benefits depending on the climate and the type of building in which it is used. Like low-density foam, medium-density spray foam is often used for continuous insulation, interior wall cavity fill, and unvented attic applications. Medium-density spray foam is a closed-cell spray foam; it is often used where there is need for the greatest R-value insulation per inch possible. Medium-density foam acts as an air, vapor, and water barrier, and can even help reduce noise, and is often not affected by moisture such as wind-driven rains.
High-Density
As its name implies, this foam has the densest structure, and it is a good choice for roofing or other exterior insulation because of its seamless, monolithic nature. High-density spray foam can help significantly reduce energy costs over a roof’s lifetime due to its thermal resistance properties. It also offers increased protection against air and water infiltration and strengthens the structure to which it is applied. The bond that spray foam forms to the roof can increase a building’s resistance to wind uplift, which can help reduce potential damage during periods of high wind. Builders often turn to high-density spray foam when extra strength is needed.


